

|
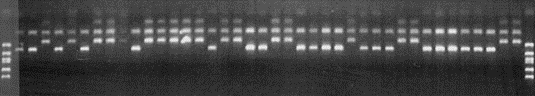
The extreme linkage disequlibrium in T. gondii simplifies strain typing as a small set of markers can be used to establish the genotype of new isolates. A variety of techniques have been described, but one of the most straight forward methods is PCR amplification followed by restriction fragment polymorphism (RFLP) analysis. This method takes advantage of the fact that single nucelotide polyorphisms (SNPs) occur every ~1 / 100 bp between the three main lineages of T. gondii. A large number of SNP markers are available for genetic mapping in T. gondii; however most of these markers lack the sensitivity for analysis of clinical samples. Consequently, we have developed a number of unlinked markers for senstive genotyping of T. gondii using a nested PCR strategy.
Protocols for analysis of clinical samples are provided for nested PCR markers.
Listing of T. gondii samples that
have been genotyped  .
.

Department of Molecular Microbiology
Washington University School of Medicine
St. Louis, MO USA
