|
|
Genomes
|
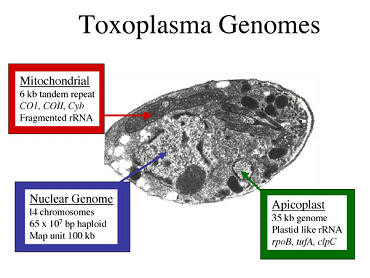
T. gondii contains three separate genomes: the nuclear genome, consisting of at least 14 chromosomes, the mitochondrial genome, and the apicoplast. The nuclear genome is haploid and consists of ~65 mB of DNA, organized into 14 distinct chromosomes. |
|
|
The mitochondrial genome is not well studied, but based on analogy to Plasmodium, it may consist of a tandem repeat (Joseph et al. 1989). The apicoplast is a vestigal endosymbiont (Maréchal and Cesbron-Delauw 2001) containing a stream-lined 35 kb circular genome. Many genes formerly encoded on the apicoplast have been transferred into the nucleus (Foth et al. 2003). Genetic studies in Plasmodium have shown that the mitochondrion (Creasey et al. 1993), and likely the apicoplast, are inherited unipartentally during sexual crosses. |
||
Department of Molecular Microbiology
Washington University School of Medicine
St. Louis, MO USA