|
| Genetic Crosses between types II and
III Table 1 Results of IIxIII crosses
|
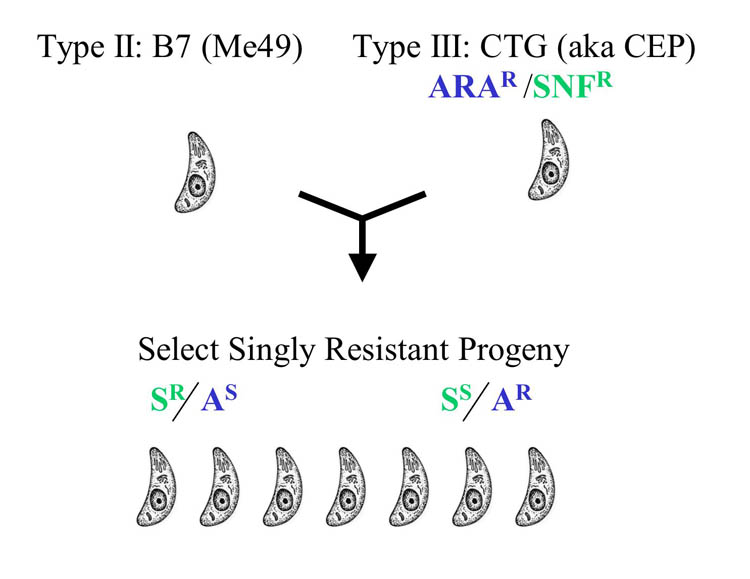
The initial genetic cross was performed between the type II strain Me49 and the type III strain CEP in a project conducted jointly between Dr. John Boothrooyd’s laboratory at Stanford University and Dr. Elmer Pfefferkorn at Dartmouth University. Prior to being used in the cross, the Me49 strain was passed through a cat to obtain a clone that was capable of completing the life cycle. This clone was referred to as B7 (aka PDS) and it was subsequently used for the whole genome and EST sequencing. Recombinant clones were obtained from two parellel crosses (S and CL) by selecting singly resistant progeny using the markers adenine arabinoside (ARA), and synefungin (SNF) resistance. The segregation patterns of 64 markers among the 19 progeny were used to construct rudimentary linkage maps (Sibley et al. 1992). In total, 11 chromosomes were identified, most of which were also physically anchored by hybridization of probes to pulse field gels (Sibley and Boothroyd 1992). |
|||||||||||
|
|
A second cross was subsequently performed by Dr. E. Pfefferkorn using a similar strategy (referred to as c96). Recombinant clones were obtained by selecting doubly resistant progeny using the markers arprinocid (APO) and synefungin (SNF) resistance. The numbers of recombinant progeny (F1) analyzed from these two crosses are summarzed in Table 1. These progeny have been analyzed using an expanded set of PCR-based markers summarized in the Toxoplasma Genome Mapping Database. |
|||||||||||
Department of Molecular Microbiology
Washington University School of Medicine
St. Louis, MO USA